What type of business to choose in Vietnam?
- 7:39 am
- admin
As a foreign investor wanting to do business in Vietnam, the first thing you must decide is to choose the most suitable business type for your company.
In this content, GTax will introduce and compare two popular business types in Vietnam that foreign investors often choose and their importance to your business.
There are 2 common types of businesses in Vietnam: Joint Stock Company (JSC) and Limited Liability Company (LLC). Therefore, this article will discuss this issue and help investors better understand investment forms in Vietnam.
Joint stock companies (JSC)
A Joint Stock Company (JSC) is a legal entity whose charter capital is divided into shares held by three or more Organizations and/or Individuals (Shareholders). Shareholders are responsible for the debts and liabilities of the company to the extent of the amount of their contributed capital. A JSC may issue stock in order to raise capital, and it may list on the Stock Exchange.
Types of shares of a JSC are: ordinary shares, dividend preference shares, redeemable preferred shares, voting preference shares, and other preferred shares as prescribed in the company’s charter and the Law on Securities.
A joint stock company can be desribed as follows:
- Charter capital is divided into equal parts called shares;
- Shareholders are only liable for debts and other property obligations of the enterprise to the extent of the amount of capital they have contributed to the enterprise;
- Shareholders have the right to freely transfer their shares to others, except in cases where shareholders own voting preference shares;
- Shareholders can be organizations or individuals. The minimum number of shareholders is three and there is no limit to the maximum number.
- A joint stock company has legal status from the date of issuance of the business registration certificate. Joint-stock companies have the right to issue stocks to the public in accordance with the law on securities.
- Charter capital of a joint-stock company is the total par value of shares of all kinds sold. Charter capital of a joint-stock company at the time of business registration is the total par value of shares of all kinds which have been registered for purchase and recorded in the company’s charter. Shareholders must pay in full for the number of shares registered for purchase within 90 days from the date of issuance of the Certificate of Business Registration.
- A joint stock company must have a General Meeting of Shareholders, a Board of Directors, a Supervisory Board and a Director or General Director. In case a joint-stock company has less than 11 shareholders and the shareholders are organizations holding less than 50% of the total shares of the company, it is not required to have a Supervisory Board.
- Type 1: The General Meeting of Shareholders, Board of Directors (BOD), Supervisory Board, and (General) Director. In case the JSC has less than 11 shareholders and the shareholders that are organizations holding less than 50% of the total shares of the company, it is not required to have a Supervisory Board;
- Type 2: The General Meeting of Shareholders, Board of Directors (BOD), and (General) Director. In this case, at least 20% of the members of the BOD must be independent members and have an Audit Committee under the BOD.
The annual General Meeting of Shareholders shall be held if the attendance rate is at least 51% of the total number of voting shares. If the first meeting fails to meet this attendance rate, the rate for the second meeting is at least 33% of the total number of voting shares. If the second meeting fails to meet this rate, the third meeting will be held irrespective of the attendance rate.
- Types of shares and the total number of shares of each;
- Changing scopes of business;
- Changing the organizational or management structure;
- Invest in projects, or sell assets with a value of 35% or more of the total value of assets recorded in the company’s latest financial statement;
- Reorganization, dissolution of the company;
- Other matters are provided in the company’s charter.
Limited liability companies (LLC)
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) is an incorporated company with limited liability and the investor does not intend to become a publicly traded company.
Normally, foreign investors who want to establish a Limited Liability Company in Vietnam will consider ‘100% Foreign-Owned Enterprise‘.
An LLC may take the form of either an LLC with two or more members (“Multiple Member LLC”) or an LLC with one member (“Single Member LLC”).
An LLC has the status of a recognized legal entity and a member of a LLC is responsible for the debts and liabilities of the enterprise to the extent of the amount of capital that the member has contributed or committed to contribute to the enterprise. An LLC does not issue shares.
a. Multiple member LLC:
- Company Members may transfer a part of a whole capital contribution to another member(s). Current members have a priority “Right of First Refusal” and “Right of First Offer”;
- The company can raise capital by increasing the contributed capital of members, raising the contributed capital from new members, or issuing bonds;
- The company may reduce its charter capital;
-
A resolution of the Members’ Council shall pass when it is approved by the number of members owning at least 65% of the charter capital.
A Multiple member LLC has a simpler management structure than a Joint Stock Company, which is: Members’ Council, President of the Members’ Council, and (General) Director.
b. Single member LLC:
- The Company Owner has autonomy with regard to decisions made about the company, such as amending the Company’s charter, deciding business plans, appointing directors, restructuring the company, enjoying profit, and dissolving the company;
- The company may reduce its charter capital; or raise capital by the owner contributing additional capital, or issuing private bonds, but not issuing shares.
- Type 1: President and (General) Director; or
- Type 2: Members’ Council and (General) Director.
General features of limited liability company:
- The company has legal status from the date of issuance of the business registration certificate;
- Founders can be an individuals or organizations;
- Members are responsible for debts and other property obligations to the extent of the capital contributed to the enterprise;
- A limited liability company is not entitled to issue shares to raise capital.
Comparison between company types
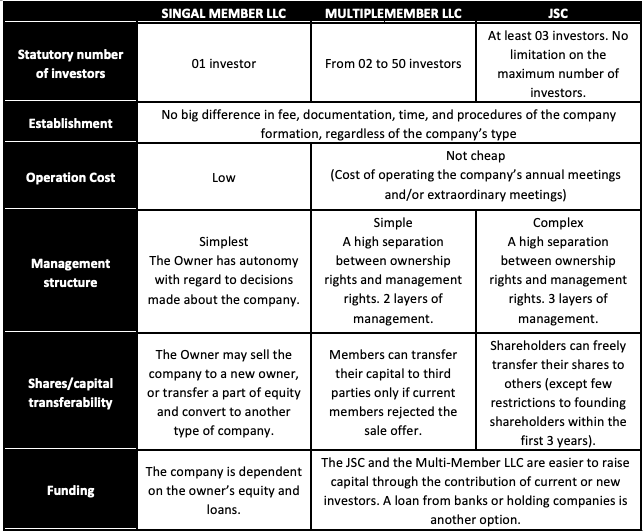
When using GTax’s services, Consultants will help you consider the advantages and disadvantages of each option and advise you on the best solution for your needs.
How to establish a business in Vietnam?
Following are the steps for your reference:
- Decide on the scope of your business;
- Rent a business location;
- Choose company type;
- Decide on the company name and capital structure;
- Apply for Investment Registration Certificate (IRC);
- Apply for Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC);
- Open a business bank account;
- Complete all post-incorporation requirements.
Compiled by GTax Accounting Service

The best type of business in Vietnam
Have you decided what type of business you want to establish in Vietnam? Choosing the best form of business entity depends on your goals, budget, risk appetite, and industry. There

Personal Income Tax (PIT) in Vietnam
With the content of this article, GTax will provide you with an overview of Vietnam’s Personal Income Tax policy. Because personal income tax (PIT) policy frequently changes, currently (2023) what

Forms of business in Vietnam
Are you planning to establish a company in Vietnam? Have you decided what form of business you want to establish in Vietnam? Are you still confused about the types of
-
How To Make Investment In Vietnam
-
Designing Functional Home Offices
-
Setting up a home office: How much does it cost?
-
How to setup a new company in Vietnam
-
Compare office rental prices in Ho Chi Minh City for foreign businesses starting a business
-
Head office registration requirements for newly established companies in Vietnam
-
The difference between a Representative Office and a Foreign Invested Company
-
A step-by-step guide to starting a business in Vietnam
-
What type of business to choose in Vietnam?
-
Forms of business in Vietnam
